TU-160M: The Modernization of a Supersonic Bomber
The Tupolev TU-160, often called the White Swan because of its sleek design, is a supersonic strategic bomber that has been part of the Russian Air Force since its introduction in the 1980s. It’s known for its variable-sweep wing, speed, and impressive payload capacity. Recent upgrades have led to the development of the TU-160M variant. This modernized version reflects advances in avionics, weapons systems, and efficiency.
Background and Development

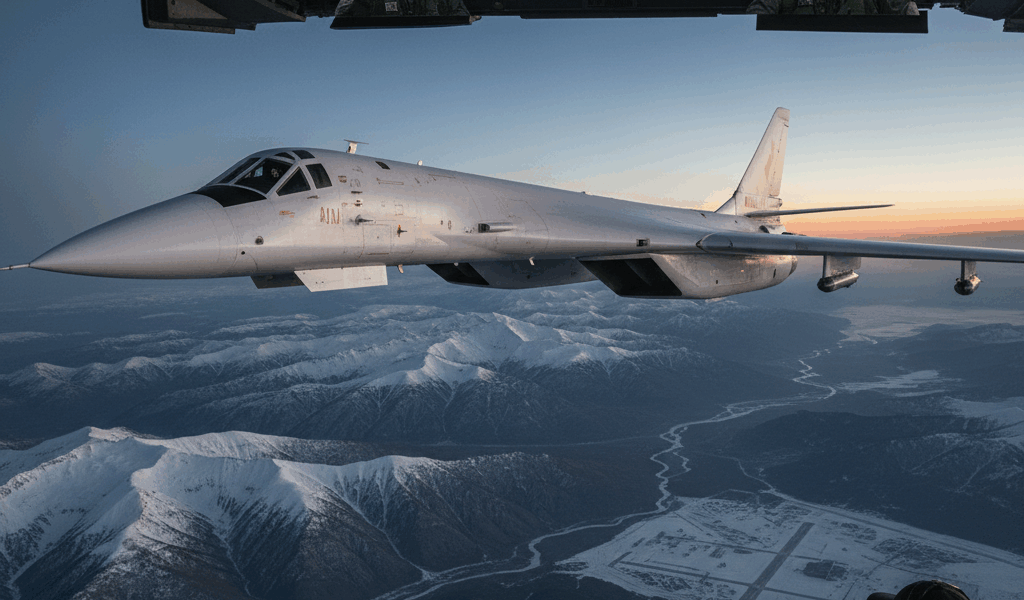
Initially designed during the Cold War, the TU-160 was built to penetrate enemy airspace at high speeds and altitudes, delivering nuclear or conventional payloads. Unlike subsonic bombers, the TU-160 has the capability of reaching speeds of Mach 2, making it difficult to intercept. The Soviet Union began developing it as a response to the United States’ B-1 bomber. Its first flight was in 1981, and it was officially introduced into service in 1987.
Only about 36 of the original TU-160 bombers were built. After the Cold War ended, production was limited due to economic constraints. However, the existing fleet continued to serve prominently in Russia’s strategic bomber force.
Modernization to TU-160M
The TU-160M represents a significant overhaul of the existing fleet, incorporating new technologies to enhance its performance and extend its service life. The modernization began in the mid-2000s, focusing on updating avionics, communication systems, and weaponry. The goal was to make the bomber more versatile for 21st-century missions.
- New avionics systems improve navigation and targeting, making it more efficient and reliable in various combat scenarios.
- Updated engines contribute to better fuel efficiency and increased range, allowing the bomber to operate over greater distances without needing frequent refueling.
The TU-160M’s weapon systems have also been upgraded to accommodate modern cruise missiles with increased precision and range. This gives the aircraft a significant strategic advantage, allowing it to launch attacks from safer distances, reducing the risk to the aircraft and its crew.
Improved Design and Capabilities
The modernization efforts have also focused on improving the bomber’s structural design. The airframe remains largely the same, leveraging the original design’s aerodynamic advantages. However, new materials have been introduced to decrease weight, increase durability, and improve stealth capabilities.
The variable-sweep wing remains a defining feature. By adjusting the wing’s sweep during flight, the TU-160M can optimize its performance across different phases of a mission. This capability enables superior handling in both high-speed intercept scenarios and long-duration cruise conditions.
Operational Role and Strategic Importance
The TU-160M fits into Russia’s broader military strategy as a key component of its nuclear triad. It complements land-based intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) and submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs), providing flexible and rapid response options.
Advancements in stealth technology, such as radar-absorbent materials and electronic warfare systems, reduce detection risks. This enables the TU-160M to penetrate sophisticated air defense systems, maintaining strategic deterrence and power projection capabilities.
Beyond its traditional nuclear role, the modernized bomber offers increased utility for conventional missions. The integration of advanced conventional weaponry allows it to perform precision strikes against strategic targets, supporting both strategic and tactical missions.
Production and Deployment
The production of new aircraft alongside upgrades of existing units has been undertaken by Russian aerospace organizations. State-backed initiatives have supported the development, reflecting the platform’s strategic value for Russia.
The first new-build TU-160M was unveiled in 2022, marking a significant milestone for military aviation. Subsequent test flights continue to validate the aircraft’s systems and performance enhancements compared to the legacy fleet.
Russia continues to prioritize the deployment of the TU-160M within its Air Force, replacing and supplementing older models. This ensures that the bomber fleet remains a central element of Russia’s aerial capabilities, adapting to modern challenges and technological advancements.
Global Context and Impact
The TU-160M’s development reflects broader global trends in military aviation. Nations with strategic bomber capability are modernizing their platforms to leverage new technologies. This ensures their aircraft remain relevant and effective amidst evolving threats.
The United States, for example, has been developing the B-21 Raider, set to complement its existing fleet of bombers. Similarly, China continues to advance its strategic bomber program with the H-20 aircraft under development. Such advancements highlight the arms race over maintaining aerial superiority and deterrence.
Russia’s investment in the TU-160M signals its commitment to maintaining its deterrent capabilities while projecting power globally. This dynamic plays a crucial role in geopolitical stability, influencing international relations and defense strategies across the globe.
Conclusion
While the article focuses on the technical and strategic aspects of the TU-160M, it is crucial to remember the broader implications of such military developments. Technology and strategy evolve alongside global political dynamics. The TU-160M stands as a testament to these changes, representing the intersection of history, technology, and strategy in modern military affairs.
“`
Recommended Aviation Gear
David Clark H10-13.4 Aviation Headset – $376.95
The industry standard for aviation headsets, trusted by pilots worldwide.
Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge – $25.42
The official FAA handbook – essential reading for every pilot.
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.



Stay in the loop
Get the latest wildlife research and conservation news delivered to your inbox.