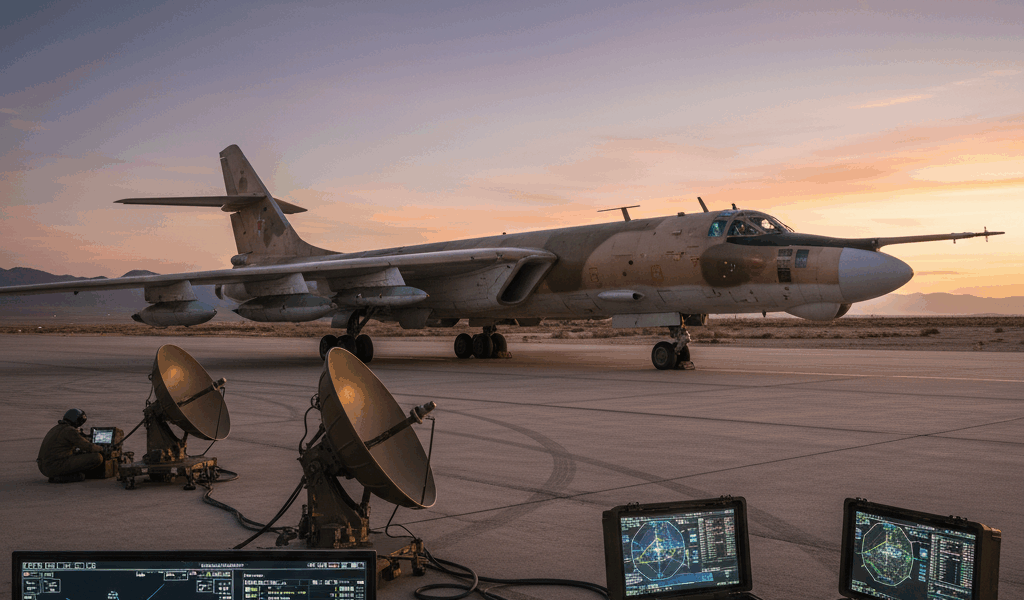
The TU-16: A Historical Overview
The Tupolev TU-16 was a remarkable aircraft from the Soviet Union. First taking to the skies in April 1952, it played a crucial role during the Cold War. Designed by Andrei Tupolev’s team, it became a versatile platform for various military operations.
Development and Design

The need for a jet-powered bomber emerged post-World War II. The Soviets sought an aircraft that could cover long distances with heavy payloads. The TU-16 was their answer. It was powered by two Mikulin AM-3 turbojet engines. These engines gave it the ability to fly great distances with significant speed for that era. Structurally, it featured a swept-wing design, which was advanced for its time. This design was pivotal for achieving higher speeds.
The initial purpose of the TU-16 was strategic bombing. However, its adaptability allowed for different configurations. It could be equipped as a missile carrier, reconnaissance plane, and even electronic warfare. The versatility of the TU-16 was a significant advantage during its operational life.
Operational History
The TU-16 entered service in 1954. It became a mainstay of the Soviet Long-Range Aviation branch. Its capability to deliver nuclear and conventional payloads made it a deterrent during the Cold War. The aircraft participated in various military exercises and missions, showcasing its range and payload capacity.
The TU-16 was not limited to the Soviet Union. It was exported to several countries, including Egypt and China. In Egypt, it played roles during conflicts with Israel. The Chinese variant, known as the Xian H-6, was produced under license and remains in service today, albeit with significant upgrades.
Technical Specifications
- Wingspan: 31.6 meters
- Length: 34.8 meters
- Height: 10.6 meters
- Maximum speed: 990 km/h
- Range: 7,200 km
- Crew: Typically 6
- Payload capacity: 9,000 kg of bombs or missiles
Roles and Variants
The TU-16 was a platform for numerous variants. Some were equipped for electronic warfare and reconnaissance. The TU-16K variant was a missile carrier, capable of launching anti-ship missiles. The diversity in roles allowed the TU-16 to stay relevant throughout its service life.
The conversion to a tanker aircraft was another noteworthy adaptation. Aircraft like the TU-16N played crucial roles in refueling missions, enhancing the reach of Soviet and allied air operations. This ability was pivotal for maintaining strategic capabilities over long distances.
Legacy and Impact
The TU-16’s impact on military aviation was significant. Its design influenced future aircraft developments. The Chinese H-6 remains a testament to the enduring legacy of the TU-16 framework. Although the Soviet variants are retired, the lineage continues.
Throughout its operational life, it remains synonymous with Soviet strategic aviation. It embodied the era’s technological advancements and geopolitical tensions. The blend of speed, range, and versatility made it a formidable asset in its time.
Maintaining the TU-16
Maintenance of the TU-16 was no small feat. It required specialized training and facilities. The complex systems needed regular checks to ensure safe operation. Periodic overhauls were necessary, involving engine inspections and structural assessments. Availability of replacement parts was crucial for maintaining operational readiness.
TU-16 in Modern Context
Even as aviation technology advanced, the TU-16 set a standard in certain aspects. Its adaptable airframe allowed it to serve various purposes over decades. Modern aircraft owe some of their design principles to lessons learned from the TU-16. Although technologically outdated by today’s standards, its legacy informs current and future developments in strategic aviation.
Recommended Aviation Gear
David Clark H10-13.4 Aviation Headset – $376.95
The industry standard for aviation headsets, trusted by pilots worldwide.
Pilot’s Handbook of Aeronautical Knowledge – $25.42
The official FAA handbook – essential reading for every pilot.
As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases.


Stay in the loop
Get the latest wildlife research and conservation news delivered to your inbox.